| 96 kHz.org |
| Advanced Audio Recording |
Introduction to 2D- quadradic residue diffusers In a former article we showed some aspects of common QR-Diffusers known as Schröder-diffusers. Here a 2D-structure is shown.
A common method of defining the wells' depth is to use the residue value of a division from the square of the coordinate and a prime figure. Unlike as with common QR-diffusers both dimensions are covered which leads to more a scattering behavior than known from 1D-QRD-Designs. Depending on the coordinate offset and the modulo value used for the division different structures can be achieved. They differ in total depth and behavior. In most cases the minimal depth is desired while slight deviation from the ideal diffusion curve is accepted. However a symmetrical design should be used.
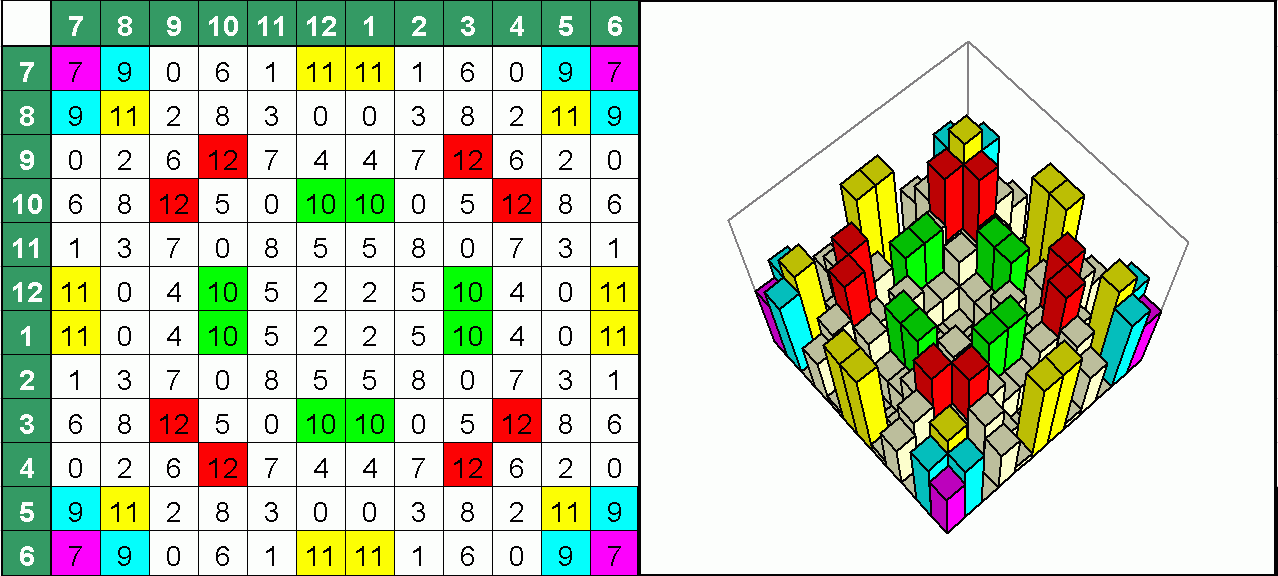
An optimized 2D-quadratic residue diffuser using 12 wells per period from 13 - fully symmetrical. Here the equation Z = (X*X + Y*Y) MOD 13 is used. The offset has been chosen that way that symmetry has been achieved. This is important because any diffusion method always will cause a signature.
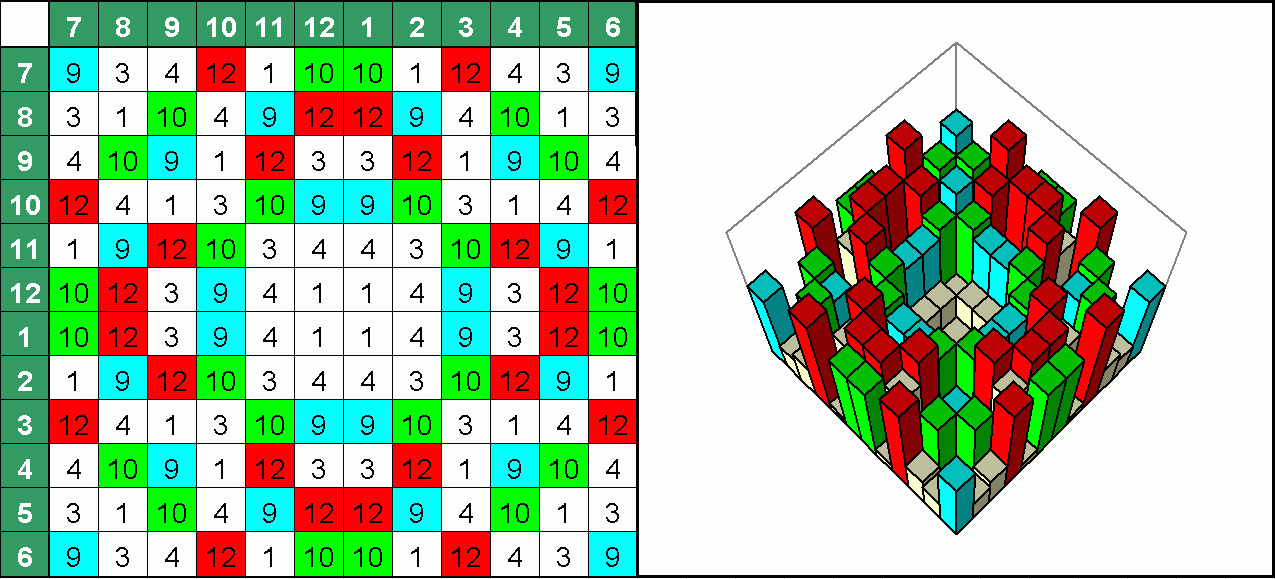
An optimized 2D-quadratic residue diffuser using 12 wells per period from 13 possible to become fully symmetrical. Unlike above the equation is Z = (X*X * Y*Y) MOD 13 but with a different Z-offset. The remarkable point is that this design does not include the value 0, which means it is not totally flat. It that can be built with just the wooden elements and does not require a back wall.
Conclusion and Summary Optimized equations can be used to obtain a fully symmetrical QRD-2D-diffuser.
See the former article about QRD-diffusers
You may also want to have a look at the article Studio Design
|
| © 2007 J.S. |