Example of sine wave generation in digital systems
The subsequent images show some examples of DDS based wave generation. See this page for more information about DDS:
Example 1
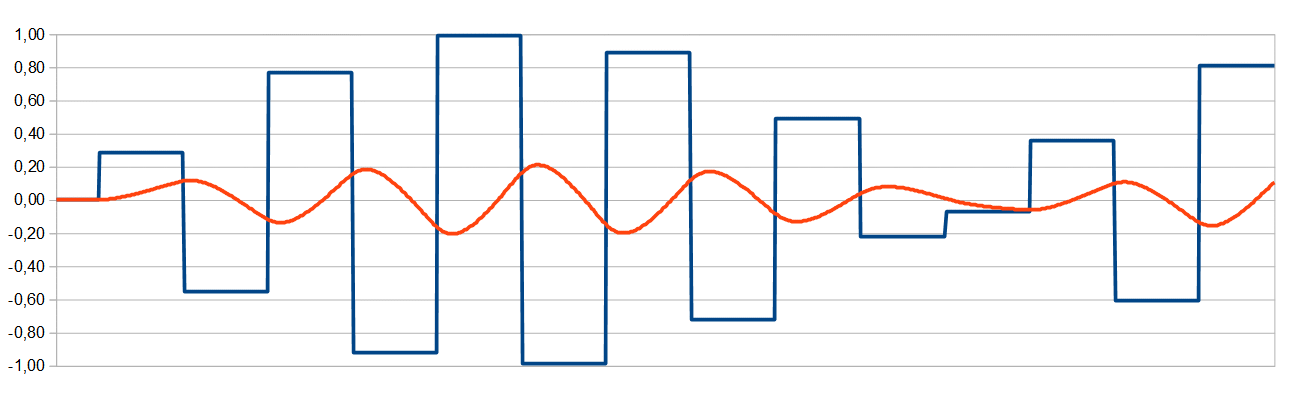
With 44,1kHz sampling frequency used for common audio recording, strong filtering will have to be applied in order to achieve a good sinus wave. Here a double T-filter is used which has a damping ratio of 1:50 (0,02 ... 0,98) in the digital domain. For audio this might be appropriate, since the optical deviation is caused be upper harmonics which are not audible. Though the analog wave has some low frequent drift. The steep filter causes also a significant phase offset.
The image shows the case for a 20kHz audio frequency. The amplitude is already reduced down to less than 50% because of the used edge frequency of the filter.
Example 2
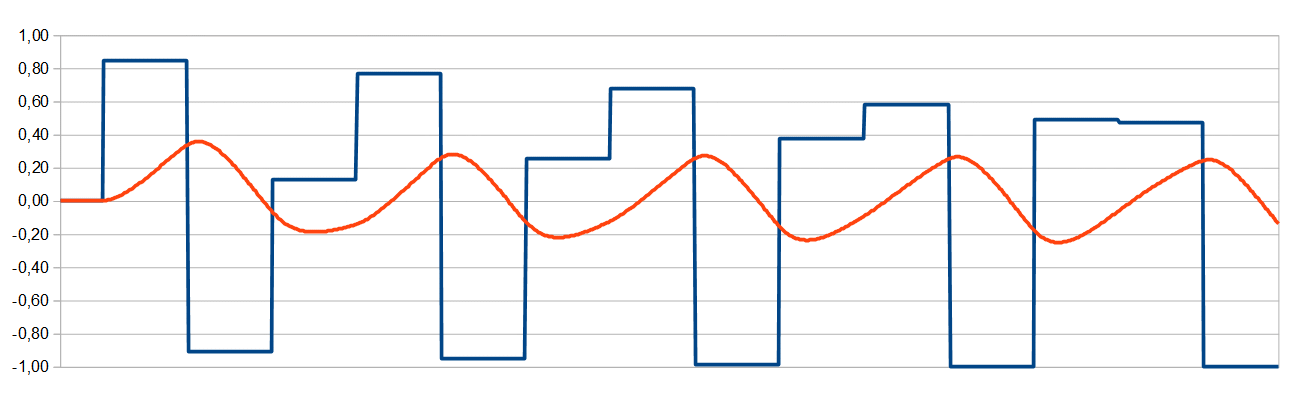
Even with 15kHz, strong deviation and phase offset, as well as low frequent drift can be observed.
Example 3
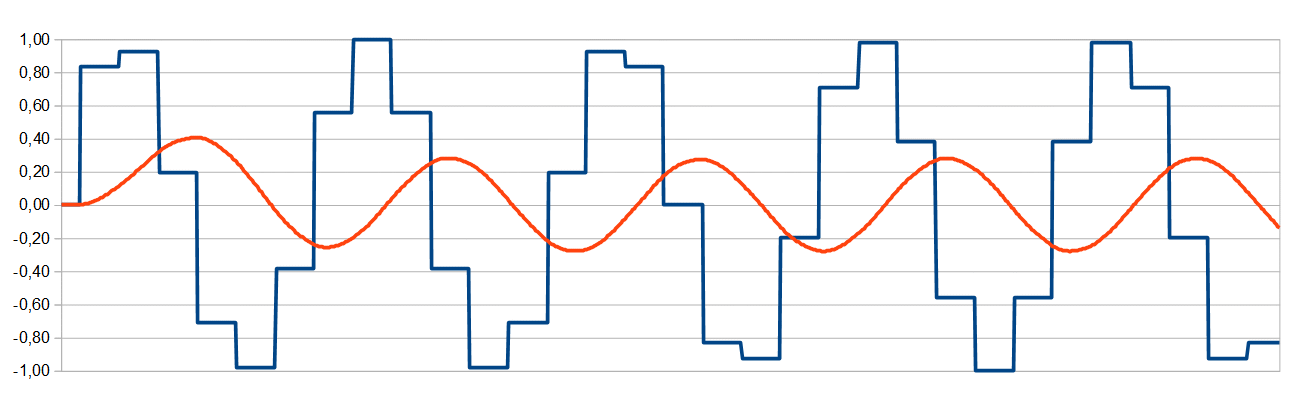
The same frequency (15kHz) generated with a sampling frequency of 96kHz shows less unwanted issues. This is even appropriate for industrial applications.
Example 4
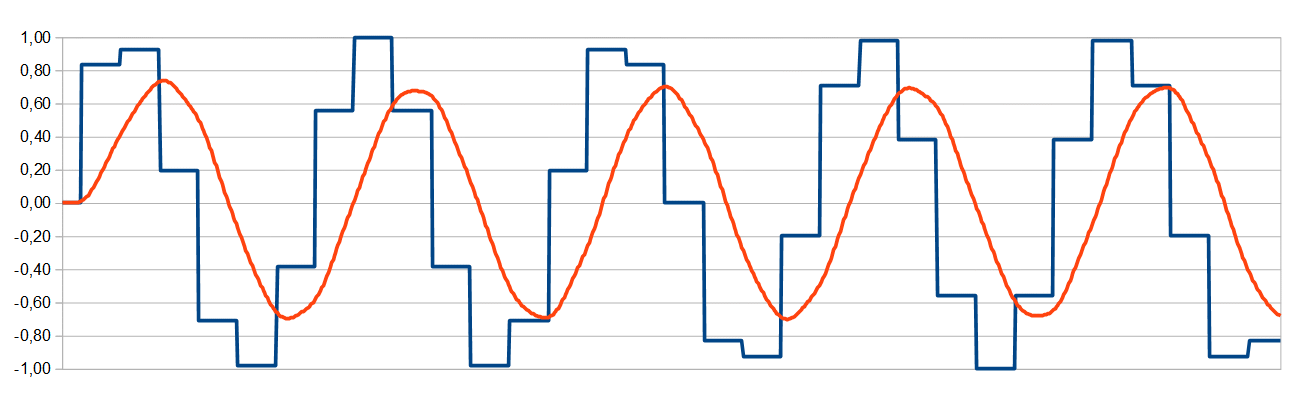
For audio only the filter can now be modified in that way, that less deviation and phase offset occurs. Here a 0,05 ... 0,95 ratio of the filter (digital representation) is used.
Example 5
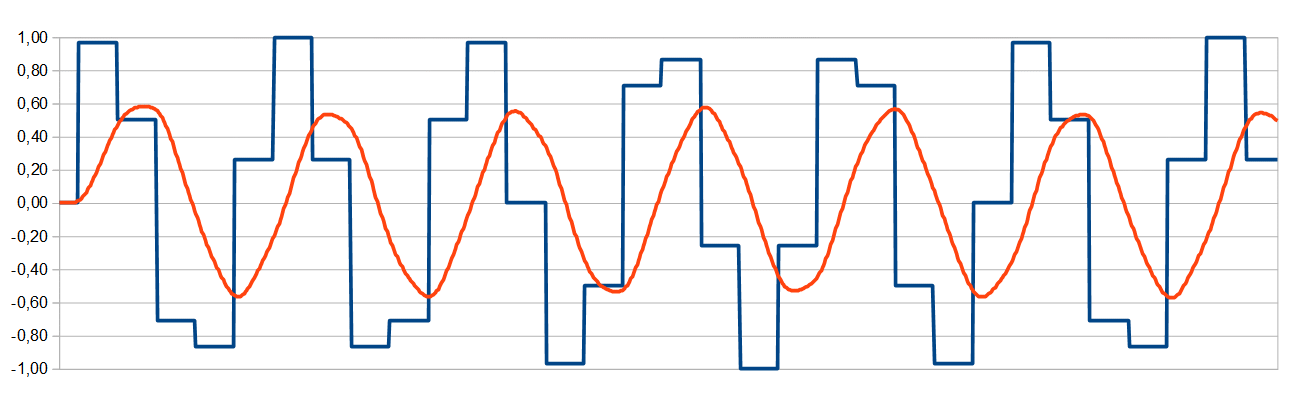
Even the 20kHz wave is pretty fine for audio now! This low distortion may be accepted for audio well.
Read about some more issues with DDS