Advanced Sound Generation with DAC-Dithering
Digital Analog Converters have a limited resolution in terms of time and amplitude. Although filters after the DAC and in the subsequent electronic circuit perform anti aliasing by limiting the resulting maximum output frequency, there are some issues which need further attention. Typically a DAC already has a well designed output filter which meets its capabilities and e.g. respects Nyquists' criteria accordingly. Oversampling and dithering is regurlarly applied inside the DAC itself to control the internal output filter in a perfect way.
In such cases where it is required to optimize a DACs behaviour according to a special spectrum or use it with additional oversampling in order to achieve even more resulition than the DAC offers at the first sight, additional treatment may applied. This especially applies to demands like a perfect sine wave with a DDS for measurement purposes or when producing precise audio.
Problems with Direct Digital Synthesis
Here a common problem with DDS is shown: There is a kind of a stairway (green) resulting in an analog value which follows in a non ideal war way because the interpolation is not well. A change of the filter edge frequency was the choice to deal with this.

Dithering helps to improve Interpolation
Dithering is used to control the anti aliasing filter by adding noise to the signal leading to a kind of PWM for the least significan bit. In this DDS-example the phase vector (dark blue) is dithered and rounded to different values (light blue). The filtered wave is more smooth. The errors are distributed over the spectrum resulting as a low noise.
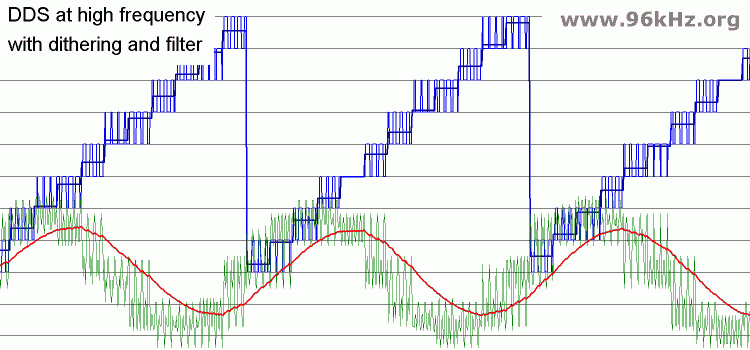
Dithering Details
The amount and spectrum of the dither noise has a strong impact on the final signal quality. For instance a higher noise level with a more complex signal can help to drive a filter in a faster way and lead to a higher precision the same time when sufficient oversampling is possible and applied. In the following examples only the two / three LSBs are used together with 1.5 / 2.5 digit dithering noise. The V2 can be used together with high oversampling rates and low resolution DACs.
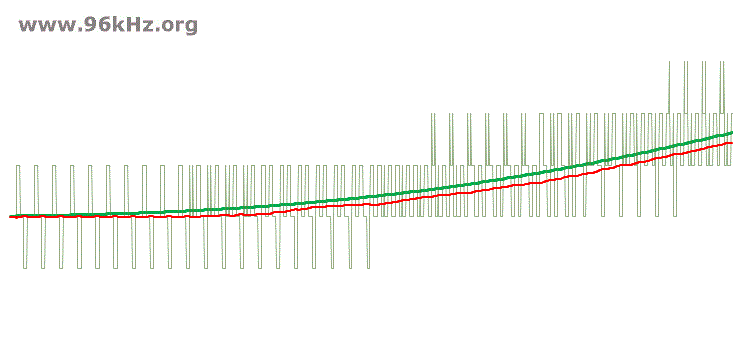
low amplitude of dither noise and high narrow spectrum - issues at low frequencies
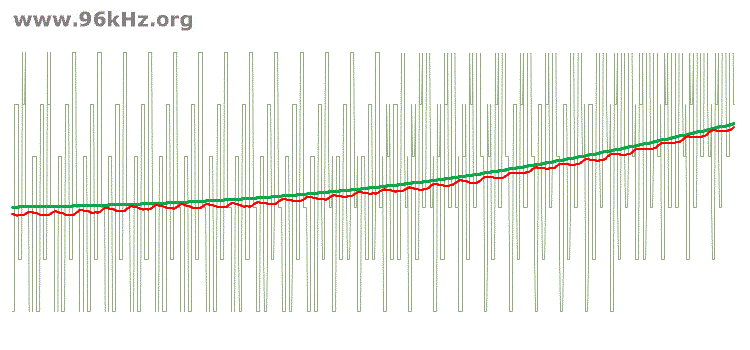
high amplitude of dither noise and wider spectrum - more noise in the high range
Conclusion
Dithering can be used to lower issues with DACs and optimize performance.
Read also Limits of DDS